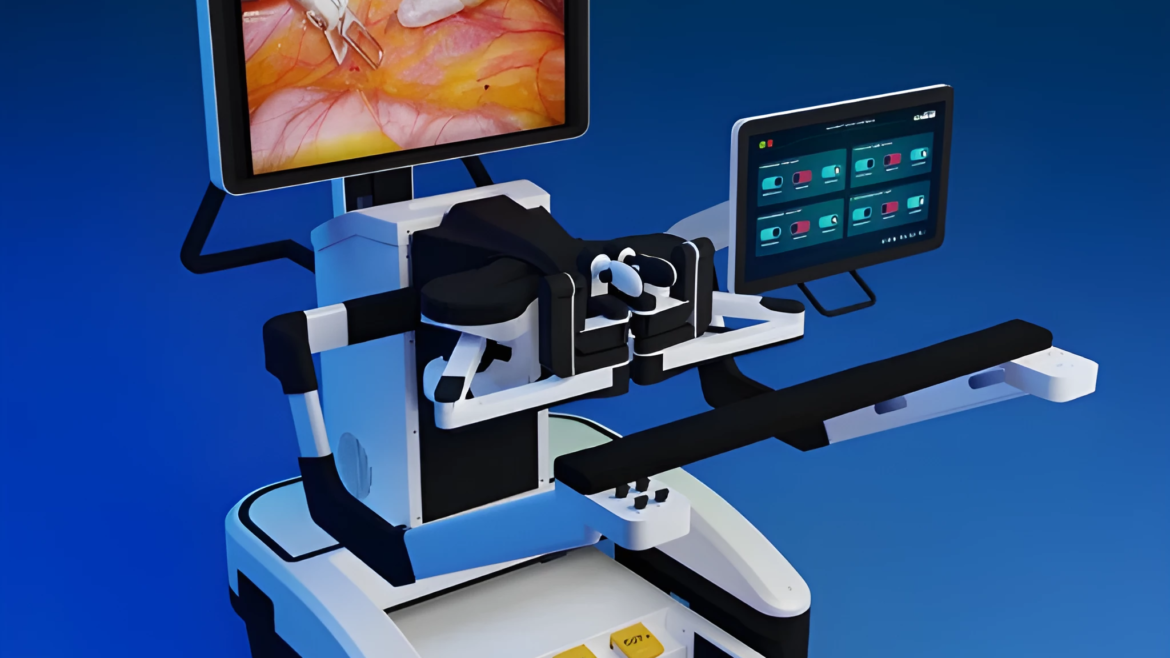
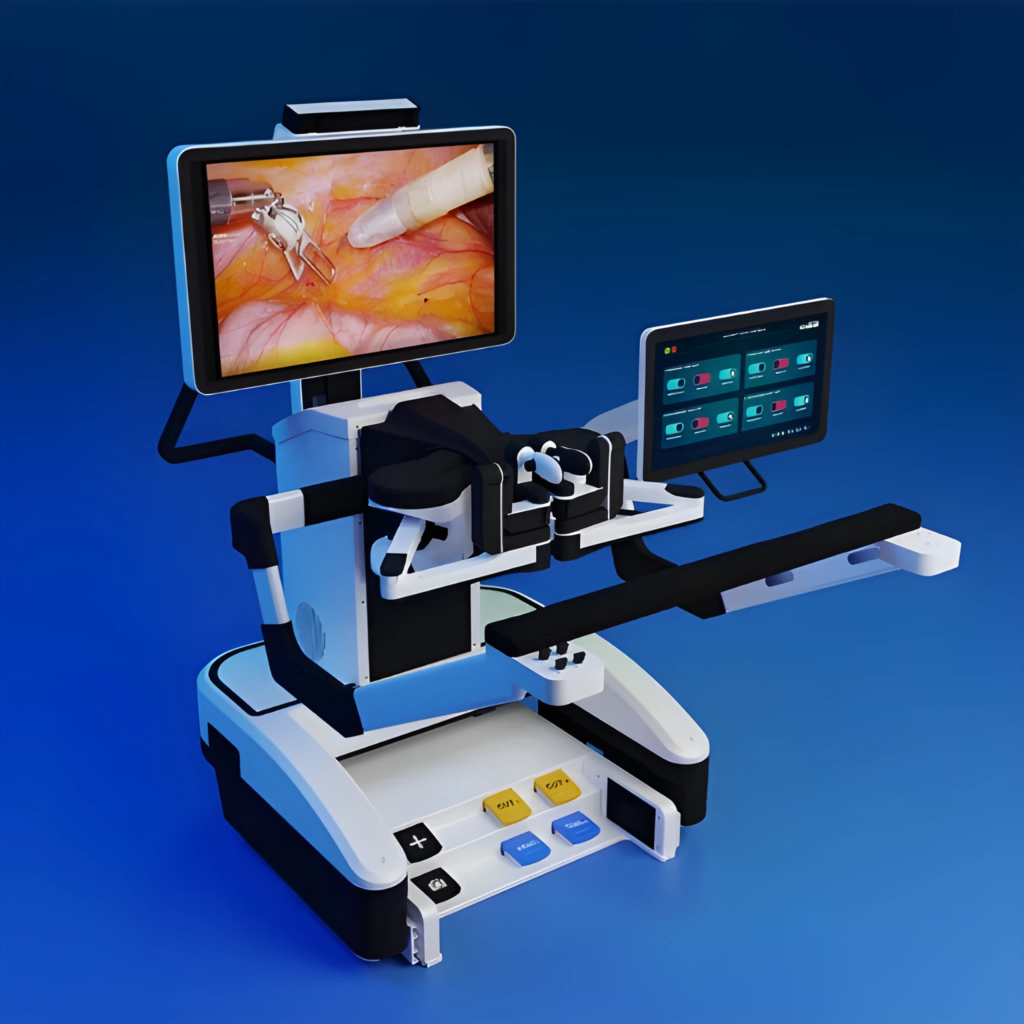
The central console or workstation where the surgeon sits during the procedure to control the robotic surgical system. This command center typically consists of several components
-
- Master Console or Control Panel: This is the primary interface where the surgeon sits. It includes hand controls, joysticks, or other input devices that allow the surgeon to manipulate the robotic arms and instruments with precision. The console may also feature foot pedals for additional control options.
- Visual Display: The surgeon command center is equipped with high-definition displays that provide real-time visual feedback from the surgical field. These displays show images captured by the robotic camera system, allowing the surgeon to view the surgical site in detail.
- Instrument Feedback: Advanced robotic surgical systems provide haptic feedback to the surgeon, allowing them to feel resistance or pressure while manipulating instruments. This tactile feedback helps the surgeon to perform delicate maneuvers with greater precision.
- Computer Interface: The command center is connected to a computer system that processes data from the robotic system and controls various functions. Surgeons may use specialized software applications to plan and execute surgical procedures, analyze imaging data, and monitor patient vitals.
- Communication System: In some cases, the surgeon command center may be equipped with communication tools that allow the surgeon to interact with other members of the surgical team, such as assistants, nurses, and anesthesiologists.
Overall, the surgeon command center serves as the nerve center of the robotic surgical system, providing the surgeon with the tools and feedback necessary to perform complex procedures with precision and accuracy.